Blank De 147 PDF Form
Embarking on the role of a personal representative within the legal proceedings of a probate case comes with an array of responsibilities and duties that are both intricate and paramount for the seamless administration of an estate. The DE-147 form, specifically tailored for use in the Superior Court of California, acts as a cornerstone document that guides appointed individuals through the multifaceted journey of estate management. It outlines the mandatory actions required by the personal representative, ranging from the initial management of the estate's assets, ensuring investments are prudent and separate from personal finances, to the intricate task of inventorying estate property. Furthermore, this form casts light on the necessity of filing an inventory and appraisal within a stipulated timeframe, notifying creditors, securing the estate with appropriate insurance, maintaining accurate records for court review, and the imperative of consulting with an attorney to navigate the legal intricacies effectively. Also included is an acknowledgment of receipt, underscoring the personal representative's understanding and acceptance of these vital duties. The DE-147 form is not merely a document; it is a comprehensive guide that underscores the significant legal and fiduciary obligations placed on the shoulders of a personal representative. Its detailed provisions ensure that individuals are well-informed of their duties, potentially mitigating legal complications by setting a clear framework for estate administration.
Document Preview Example
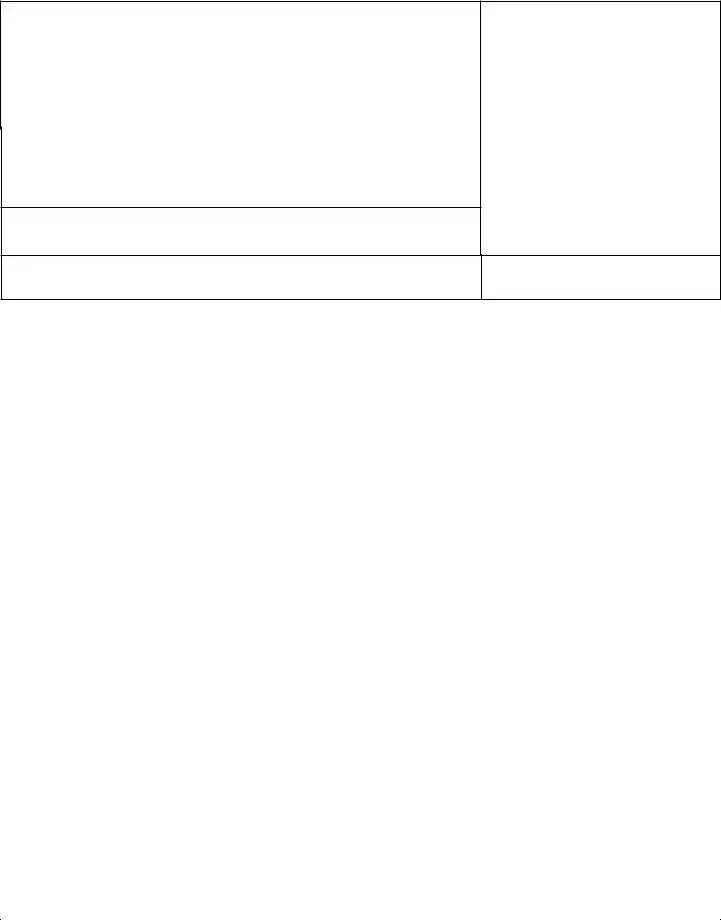
ATTORNEY OR PARTY WITHOUT ATTORNEY (Name, State Bar number, and address):
TELEPHONE NO.: |
FAX NO. (Optional): |
|
|
ATTORNEY FOR (Name): |
|
SUPERIOR COURT OF CALIFORNIA, COUNTY OF
STREET ADDRESS:
MAILING ADDRESS:
CITY AND ZIP CODE:
BRANCH NAME:
ESTATE OF (Name):
DECEDENT
FOR COURT USE ONLY
DUTIES AND LIABILITIES OF PERSONAL REPRESENTATIVE |
CASE NUMBER: |
and Acknowledgment of Receipt |
|
DUTIES AND LIABILITIES OF PERSONAL REPRESENTATIVE
When the court appoints you as personal representative of an estate, you become an officer of the court and assume certain duties and obligations. An attorney is best qualified to advise you about these matters. You should understand the following:
1. MANAGING THE ESTATE'S ASSETS
a.Prudent investments
You must manage the estate assets with the care of a prudent person dealing with someone else's property. This means that you must be cautious and may not make any speculative investments.
b.Keep estate assets separate
You must keep the money and property in this estate separate from anyone else's, including your own. When you open a bank account for the estate, the account name must indicate that it is an estate account and not your personal account. Never deposit estate funds in your personal account or otherwise mix them with your or anyone else's property. Securities in the estate must also be held in a name that shows they are estate property and not your personal property.
c.
Except for checking accounts intended for ordinary administration expenses, estate accounts must earn interest. You may deposit estate funds in insured accounts in financial institutions, but you should consult with an attorney before making other kinds of investments.
d.Other restrictions
There are many other restrictions on your authority to deal with estate property. You should not spend any of the estate's money unless you have received permission from the court or have been advised to do so by an attorney. You may reimburse yourself for official court costs paid by you to the county clerk and for the premium on your bond. Without prior order of the court, you may not pay fees to yourself or to your attorney, if you have one. If you do not obtain the court's permission when it is required, you may be removed as personal representative or you may be required to reimburse the estate from your own personal funds, or both. You should consult with an attorney concerning the legal requirements affecting sales, leases, mortgages, and investments of estate property.
2. INVENTORY OF ESTATE PROPERTY
a.Locate the estate's property
You must attempt to locate and take possession of all the decedent's property to be administered in the estate.
b.Determine the value of the property
You must arrange to have a
c.File an inventory and appraisal
Within four months after Letters are first issued to you as personal representative, you must file with the court an inventory and appraisal of all the assets in the estate.
|
|
Page 1 of 2 |
Form Adopted for Mandatory Use |
DUTIES AND LIABILITIES OF PERSONAL REPRESENTATIVE |
Probate Code, § 8404 |
Judicial Council of California |
(Probate) |
|
|
ESTATE OF (Name):
DECEDENT
CASE NUMBER:
d.File a change of ownership
At the time you file the inventory and appraisal, you must also file a change of ownership statement with the county recorder or assessor in each county where the decedent owned real property at the time of death, as provided in section 480 of the California Revenue and Taxation Code.
3. NOTICE TO CREDITORS
You must mail a notice of administration to each known creditor of the decedent within four months after your appointment as personal representative. If the decedent received
4. INSURANCE
You should determine that there is appropriate and adequate insurance covering the assets and risks of the estate. Maintain the insurance in force during the entire period of the administration.
5. RECORD KEEPING
a.Keep accounts
You must keep complete and accurate records of each financial transaction affecting the estate. You will have to prepare an account of all money and property you have received, what you have spent, and the date of each transaction. You must describe in detail what you have left after the payment of expenses.
b.Court review
Your account will be reviewed by the court. Save your receipts because the court may ask to review them. If you do not file your accounts as required, the court will order you to do so. You may be removed as personal representative if you fail to comply.
6. CONSULTING AN ATTORNEY
If you have an attorney, you should cooperate with the attorney at all times. You and your attorney are responsible for completing the estate administration as promptly as possible. When in doubt, contact your attorney.
NOTICE: 1. This statement of duties and liabilities is a summary and is not a complete statement of the law. Your conduct as a personal representative is governed by the law itself and not by this summary.
2.If you fail to perform your duties or to meet the deadlines, the court may reduce your compensation, remove you from office, and impose other sanctions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT OF RECEIPT
1.I have petitioned the court to be appointed as a personal representative.
2.My address and telephone number are (specify):
3.I acknowledge that I have received a copy of this statement of the duties and liabilities of the office of personal representative.
Date:
(TYPE OR PRINT NAME) |
(SIGNATURE OF PETITIONER) |
Date:
(TYPE OR PRINT NAME) |
(SIGNATURE OF PETITIONER) |
CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION: If required to do so by local court rule, you must provide your date of birth and driver's license number on supplemental Form
DUTIES AND LIABILITIES OF PERSONAL REPRESENTATIVE |
||||||
|
|
|
(Probate) |
|||
For your protection and privacy, please press the Clear |
|
|
|
|
|
|
This Form button after you have printed the form. |
|
Print this form |
|
Save this form |
|
|
Page 2 of 2
Clear this form
Document Specs
| Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Form Identification | DE-147, Duties and Liabilities of Personal Representative |
| Governing Law | California Probate Code, § 8404 |
| Purpose | To outline the primary responsibilities and legal obligations bestowed upon a personal representative of an estate in the State of California. |
| Key Responsibilities | Includes managing the estate's assets, inventorying estate property, notifying creditors, maintaining insurance, and keeping accurate records. |
Detailed Instructions for Writing De 147
Filling out the DE-147 form is a pivotal step for individuals preparing to undertake the duties of a personal representative of an estate. This form, a declaration of the receipt of the document outlining the responsibilities and potential risks associated with this role, serves as an acknowledgment that the person taking on these tasks has been informed of what is expected of them. It’s crucial that attention to detail and accuracy is employed when completing the form to ensure a smooth process in estate management. Here are the steps to accurately complete the DE-147 form:
- Start by filling out the section titled "ATTORNEY OR PARTY WITHOUT ATTORNEY." Include the name, State Bar number if applicable, and address. If you are managing the estate without legal representation, you will fill in your personal information in this section.
- Enter the telephone number, fax number (if available), and email address in the designated spaces.
- Fill in the attorney's name for whom you are representing in the estate matters in the "ATTORNEY FOR" field. If you are not an attorney or are filling this out on your behalf, you may leave this field blank.
- In the "SUPERIOR COURT OF CALIFORNIA, COUNTY OF" section, write the name of the county where the estate proceedings are taking place.
- Provide the street address, mailing address, city and zip code, and branch name of the court handling the estate’s case.
- In the "ESTATE OF" field, input the name of the decedent whose estate is being managed.
- Write the case number associated with the estate in the "CASE NUMBER" field.
- Review the duties and liabilities of a personal representative as listed on the form. This section does not require input but should be read carefully to understand the responsibilities and legal obligations.
- Under the "ACKNOWLEDGMENT OF RECEIPT" section, acknowledge that you have petitioned to be appointed as a personal representative and have received a copy of the statement of duties and liabilities by filling in your address and telephone number.
- Sign and date the form in the designated "Date," "Type or Print Name," and "Signature of Petitioner" fields. Remember, if the form requires information about multiple petitioners, each must provide their information and signature.
- If your local court requires confidential information such as your date of birth and driver's license number, ensure you fill out and attach the supplemental Form DE-147S.
After the form is completed and signed, it should be submitted to the appropriate court in compliance with its deadlines. Make sure to retain a copy for your records. Following these instructions carefully will help ensure that your acknowledgment of the duties and liabilities as a personal representative is properly documented, paving the way for a responsible and informed administration of the estate.
Things to Know About This Form
What is the DE-147 form?
The DE-147 form, also known as the Duties and Liabilities of Personal Representative form, is a legal document used in the state of California. When appointed as a personal representative of an estate, this form outlines the responsibilities and legal obligations that the person must adhere to. It provides guidance on handling estate assets, dealing with creditors, maintaining insurance, and record-keeping, among other duties.
Who should use the DE-147 form?
This form should be used by anyone who has been appointed as a personal representative of an estate in California. This includes executors and administrators who are responsible for managing the estate of a deceased person. The form is a crucial tool for understanding the specific legal responsibilities that come with the role.
What are the key duties listed on the DE-147 form?
The key duties listed on the form include, but are not limited to:
- Managing the estate's assets in a prudent and separate manner.
- Filing an inventory and appraisal of estate property.
- Notifying creditors and handling claims against the estate.
- Maintaining adequate insurance for estate assets.
- Keeping accurate financial records and preparing accounts for court review.
- Consulting with and cooperating with an attorney if one is hired.
How does one file the DE-147 form?
To file the DE-147 form, a personal representative appointed by the court must first obtain the form, which is available through the California judicial system's website or local court. After thoroughly reading and understanding the duties and liabilities, the representative must acknowledge receipt of this information by signing the form. This signed document should then be filed with the court managing the estate's probate process. It's advisable to consult with an attorney to ensure proper completion and submission.
Is consulting an attorney mandatory for completing the DE-147 form?
While consulting an attorney is not explicitly mandatory for completing the DE-147 form, it is strongly recommended. The duties and legal obligations of a personal representative can be complex, and an attorney specializing in probčate law can provide valuable advice and ensure compliance with California law. An attorney can also assist with other aspects of estate administration, helping to avoid common pitfalls.
What are the consequences of failing to perform duties as outlined in the DE-147 form?
Failing to perform the duties as outlined in the DE-147 form can have serious consequences for a personal representative. These consequences can include reduction of compensation, removal from the position, and imposition of other sanctions by the court. Such failures can also lead to personal liability for any losses incurred by the estate due to mismanagement or neglect. Hence, understanding and adhering to the duties listed in the form is crucial for anyone serving as a personal representative.
Common mistakes
Filling out legal forms is a critical step in managing legal matters, but mistakes can easily occur, especially with forms like the DE-147, which involves the intricate details required in probate proceedings. Here are eight common errors to watch for:
- Not clearly specifying the personal information at the beginning of the form. This includes failing to list the full legal name, contact information, and, if applicable, the state bar number of the attorney or party acting without an attorney.
- Leaving the estate and decedent information blank or incomplete. This section requires detailed information about the estate in question and is crucial for the form’s validity.
- Mismanagement of the estate's assets section by failing to indicate how assets are separately maintained, or inaccurately reporting the estate’s investments and accounts, can lead to serious legal complications.
- Omitting details about the inventory and appraisal of the estate’s property. It's essential to accurately report attempts to locate, take possession, and determine the value of all property to be administered.
- Incorrectly handling the Notice to Creditors section. This includes not notifying known creditors or the State Director of Health Services in the case of Medi-Cal assistance, within the specified timelines.
- Failing to properly address the insurance coverage for the estate, thereby leaving the estate’s assets and risk coverage inadequately detailed.
- Inaccurate record-keeping and account details. It is vital to maintain detailed financial transaction records and to prepare accurate accounts of all money and property received and spent.
- Missing the acknowledgment of receipt sign-off at the end of the form. This part confirms the understanding and acceptance of the duties and liabilities as a personal representative.
These mistakes can lead to delays, additional legal fees, or more severe legal repercussions, emphasizing the importance of handling the DE-147 form with precision and care.
Documents used along the form
When navigating the probate process, the DE-147 form, "Duties and Liabilities of Personal Representative," marks a crucial step for personal representatives in understanding their responsibilities. However, this document is often just the beginning. Several other forms and documents typically accompany the DE-147 form to ensure comprehensive management and legal compliance of an estate during the probate process.
- DE-111 Petition for Probate: This petition is used to initiate the probate process. It requests the court to officially appoint the petitioner as the executor (if there's a will) or administrator (if there's no will) of the estate.
- DE-120 Notice of Petition to Administer Estate: Provides notice to interested parties that a petition for probate has been filed. This method ensures that all potential heirs or creditors are informed and have the opportunity to contest the probate filing.
- DE-160 Inventory and Appraisal: Details the assets within the estate. A personal representative is required to list all assets and have them appraised to determine their total value, aiding in the proper management and distribution.
- DE-260 Petition to Determine Succession to Real Property: Used in estates valued at $150,000 or less to transfer real property, simplifying the process for smaller estates.
- DE-285 Declaration of Completion of Probate: Filed at the end of the probate process, this declaration informs the court that all duties have been fulfilled, allowing for the formal closing of the estate.
- DE-295 Report of Sale and Petition for Order Confirming Sale of Real Property: If the estate holds real estate that must be sold, this document reports the sale to the court and requests formal approval to finalize the transaction.
Together, these documents facilitate the structured and legal management of an estate through probate. Personal representatives must be conscientious in completing and filing each relevant form, adhering to timelines, and ensuring thorough communication with the court and interested parties. This administrative diligence safeguards the estate's assets, honors the decedent's wishes, and provides clear passage through the complexities of probate law.
Similar forms
The DE-147 form, important in the administration of estates, has close similarities to a variety of other legal documents that govern how representatives or parties handle someone else’s property or interests. One such similar document is the Last Will and Testament. This crucial document outlines the deceased's wishes regarding the distribution of their estate and the care of any minors. Like the DE-147 form, it outlines specific duties and guidelines for the appointed executor (a role broadly similar to the personal representative mentioned in DE-147), guiding them in the proper management, distribution, and care of the estate's assets in accordance with the decedent’s wishes.
Similarly, the Power of Attorney (POA) document shares foundational resemblances with the DE-147 form in that it appoints an individual to manage the affairs of another person. However, unlike the DE-147, which is activated upon a person’s death, a POA is generally used while the grantor is still alive but may be incapacitated or otherwise unable to manage their affairs. The appointed attorney-in-fact or agent is entrusted with duties that may range from managing financial accounts to making healthcare decisions, emphasizing the necessity for prudent and responsible management of the principal’s assets and care.
A Trust document is another legal instrument with parallels to the DE-147 form, particularly in its stipulation of duties and responsibilities for the trustee. Trustees are appointed to manage trust assets for the benefit of the beneficiaries, similar to how a personal representative manages a decedent's estate. Both roles demand a high degree of fiduciary responsibility, requiring the acting individuals to adhere strictly to the principles of good faith, prudence, and loyalty to the interests of the beneficiaries or the estate, respectively.
The Probate Court Letters document, which officially appoints an individual as an executor or personal representative of an estate, is directly related to the DE-147 in function and purpose. This document not only confirms the appointment and authority of the personal representative but also signifies the beginning of their duties as delineated in the DE-147 form—such as inventorying assets, paying debts, and ultimately distributing the estate according to the decedent’s will or state law.
Lastly, the Notice to Creditors document is closely related to the DE-147 form concerning the responsibilities it outlines for estate administration. After being appointed, personal representatives use this document to notify all potential creditors of the decedent’s passing and the initiation of probate proceedings. This step is imperative as it allows creditors to come forward with claims against the estate, a process that the DE-147 form hints at by mandating the personal representative to settle with creditors as part of their duties in managing the estate’s liabilities and obligations.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the DE-147 form, which pertains to the duties and liabilities of a personal representative in the State of California, there are critical do's and don'ts to consider for ensuring the process is handled correctly and legally. Here are 10 essential tips:
- Do thoroughly review the form and instructions provided to understand the specific requirements and information needed.
- Do fill out the form with accurate and complete information, particularly your contact details and any pertinent case numbers.
- Do consult with an attorney if you have any doubts or questions, especially concerning the estate's assets, investments, and the specific legal duties you assume as a personal representative.
- Do keep detailed records of all estate transactions, including receipts and documentation, as you will need to account for these in court.
- Do notify known creditors and the State Director of Health Services (if applicable) in the mandated time frames.
- Don't mix estate assets with personal funds. Always maintain separate accounts to avoid confusion and legal complications.
- Don't delay in filing necessary documents, such as the inventory and appraisal of estate assets, and the notice to creditors.
- Don't make unauthorized payments or transactions with the estate's assets without court approval or legal advice.
- Don't neglect the requirement to file a change of ownership statement for any real property owned by the decedent.
- Don't forget to maintain adequate insurance coverage on estate assets as required, ensuring the protection of both your interests and those of the estate.
By following these guidelines, personal representatives can better navigate their roles with confidence, staying compliant with the law while managing the estate efficiently and responsibly.
Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions about the DE-147 form, which outlines the duties and liabilities of a personal representative in the probate process. Let's clarify these common misunderstandings:
- It's only for attorneys. While the form mentions attorneys, it's actually meant for any personal representative — someone appointed to manage the estate of a decedent, whether they're an attorney or not.
- It allows the personal representative to manage the estate freely. Contrary to what some might think, the personal representative’s powers are quite restricted. They must manage the estate's assets prudently, keep them separate from their own, and cannot make speculative investments.
- Estate assets can be mixed with personal funds. This is incorrect. The form clearly states that estate assets must be kept separate from the personal representative’s assets to avoid any confusion or misuse of funds.
- Personal representatives can pay themselves at any time. In fact, they must obtain court permission to pay themselves or their attorney fees, emphasizing the need for judicial oversight in estate management.
- Investments are freely allowed. The form explicitly requires that investments be prudent and in the best interest of the estate, with certain restrictions applied to ensure the estate is not exposed to high-risk ventures.
- No legal counsel is needed. While not explicitly stated, consulting with an attorney is highly recommended to navigate the complex legal landscape and ensure compliance with all statutory requirements.
- Filing an inventory or appraisal is optional. Within four months after being appointed, a personal representative must file an inventory and appraisal of the estate's assets with the court — this is mandatory, not optional.
- Notices to creditors are discretionary. Another misconception is that notifying creditors is at the personal representative's discretion. In reality, they are required to notify all known creditors, including the State Director of Health Services if the decedent received Medi-Cal assistance.
- Record keeping is informal. The form details the need for meticulous record keeping and accurate accounts of financial transactions. These records are subject to court review, contradicting any notion that the process is informal.
Clearing up these misconceptions is crucial for anyone involved in the probate process to understand their responsibilities and the scope of their role as a personal representative. It underscores the importance of adhering to legal requirements and ensuring the estate is managed with care and fidelity.
Key takeaways
Understanding the DE-147 form and the role of a personal representative in managing an estate is crucial. Here are seven key takeaways to consider:
- Prudent Management of Estate Assets: As a personal representative, you are expected to manage the estate's assets with the utmost care, as if managing someone else's property. This includes making prudent investments and keeping estate assets separate from personal assets. Speculative investments are off-limits, and estate accounts must be clearly identified as such.
- Inventory and Appraisal of Assets: One of your first duties will be to locate all of the decedent’s property and arrange for a court-appointed referee to appraise its value. You are responsible for filing an inventory and appraisal of all estate assets with the court within four months after receiving your appointment letter.
- Notification of Creditors: It's your responsibility to notify each known creditor of the decedent by mailing them a notice of administration. This must be done within four months of your appointment. Additionally, if the decedent received Medi-Cal assistance, the State Director of Health Services must be notified within 90 days.
- Maintaining Insurance: Ensuring appropriate and adequate insurance coverage for the estate's assets and any associated risks is crucial. You must maintain this insurance throughout the entire administration period.
- Record Keeping: Keeping complete and accurate records of every financial transaction is essential. This includes documenting all money received and spent, as well as providing detailed descriptions of the estate’s financial status.
- Court Review: The court will review your accounts, so it's important to save receipts and meticulously record every transaction. Failure to file accounts as required can lead to being ordered by the court to do so, or even removal from your position.
- Consulting an Attorney: Cooperation with your attorney, if you have one, is essential. Both you and your attorney are responsible for completing the estate administration efficiently. When in doubt, it's always best to consult your attorney for guidance and clarification.
Note that the DE-147 form also includes an acknowledgment that these duties and liabilities have been received and understood. Additionally, if local court rules demand, personal representatives might need to provide confidential information such as date of birth and driver's license number on a supplemental form.
Finally, remember that this overview is a succinct summary and not a comprehensive guide. The laws governing your conduct as a personal representative are detailed in full by the legal code itself, not just by this summary. If deadlines are missed or duties are not performed, the court may impose penalties, including reducing your compensation or removing you from your office.
Discover More PDFs
Why Don't I Qualify for Dependent Care Credit - Detailed records of care expenses and provider information ensure compliance and accurate credit calculation.
Covid Workers Compensation - Suggests prompt filing of subsequent forms for continued compensation beyond the initial 45-day period, avoiding interruption in benefits.
