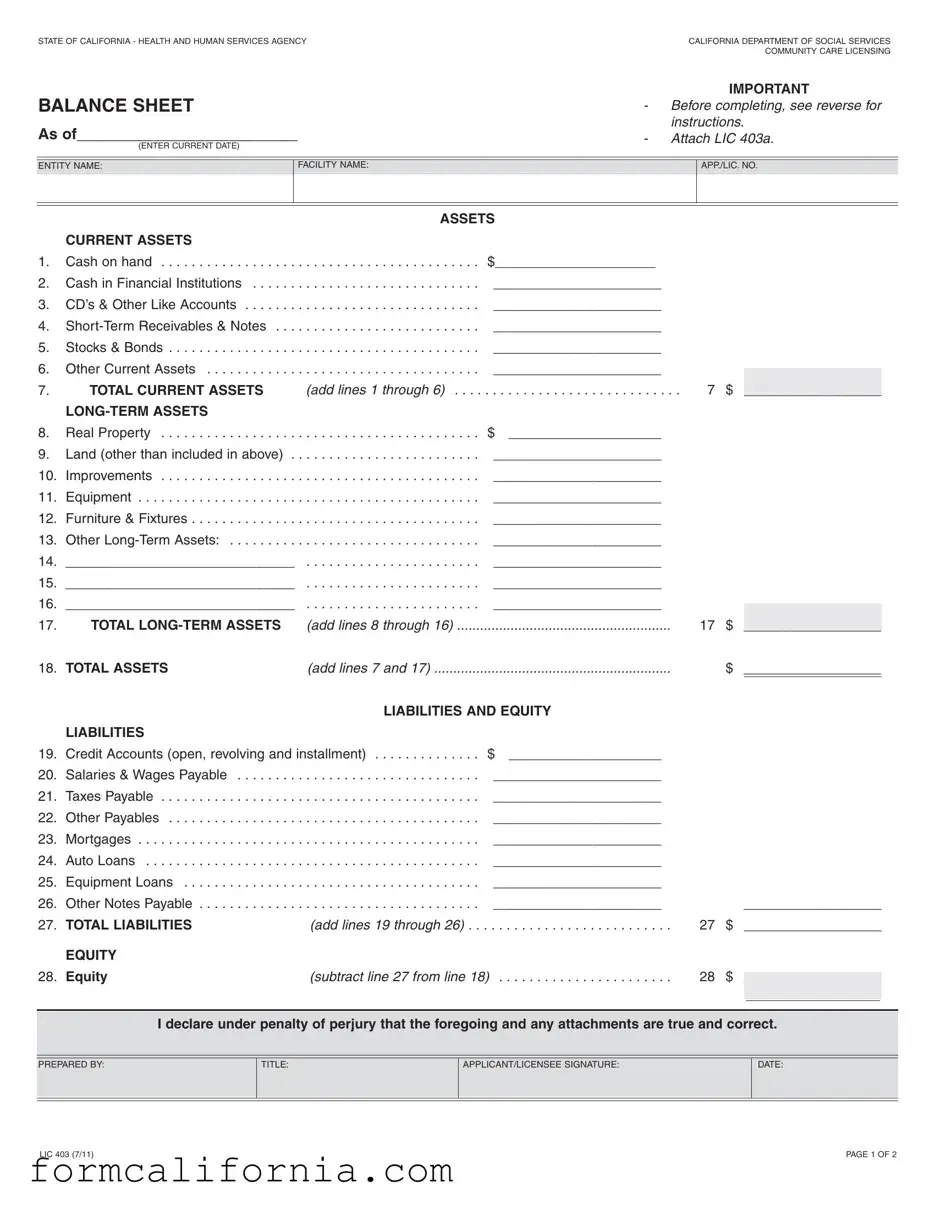
Blank California Balance Sheet PDF Form
The California Balance Sheet form, developed by the California Department of Social Services Community Care Licensing, is a critical financial reporting tool for entities within the state's health and human services sector. The intricately designed form demands comprehensive financial disclosures, spanning from current and long-term assets to liabilities and equity, to offer a full picture of an entity's financial health. A unique aspect of this form is its inclusivity, requiring detailed information not just about the care facility's direct finances but also about the personal financial positions of proprietors, partners, or corporate entities involved. This ensures a thorough vetting process, especially significant for entities involved in the sensitive area of community care. The form, which must be filled out with current and accurately calculated data, underscores the state's commitment to financial transparency and accountability, mandating the inclusion of assets ranging from cash on hand to real property, and liabilities from credit accounts to long-term notes payable. Additionally, the LIC 403a, a supplementary schedule, aids in the meticulous preparation needed before finalizing the balance sheet. By necessitating such detailed financial disclosure, California reinforces its dedication to the protection and well-being of its most vulnerable citizens through stringent operational oversight of its community care facilities.
Document Preview Example

STATE OF CALIFORNIA - HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES AGENCY |
CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SERVICES |
|
COMMUNITY CARE LICENSING |
|
|
|
|
IMPORTANT |
|
BALANCE SHEET |
- |
Before completing, see reverse for |
|||
As of__________________________ |
|
instructions. |
|||
- |
Attach LIC 403a. |
||||
(ENTER CURRENT DATE) |
|||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENTITY NAME: |
|
FACILITY NAME: |
|
APP./LIC. NO. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Cash on hand |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
$_____________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Cash in Financial Institutions |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
CD’s & Other Like Accounts |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
||
5. |
Stocks & Bonds |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
Other Current Assets |
|
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
|
|
|
||||
7. |
TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS |
(add lines 1 through 6) . . . . |
. . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 |
$ |
|
__________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
Real Property |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
$ |
____________________ |
|
|
|
|
9. |
Land (other than included in above) . . |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
10. |
Improvements |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
11. |
Equipment |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
12. |
Furniture & Fixtures |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
13. |
Other |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
14. |
______________________________ |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
______________________________ |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
16. |
______________________________ |
|
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
|
|
|
||||
17. |
TOTAL |
(add lines 8 through 16) |
17 |
$ |
|
__________________ |
|
|
18. |
TOTAL ASSETS |
(add lines 7 and 17) |
|
$ |
__________________ |
|
||
|
|
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
||
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19. |
Credit Accounts (open, revolving and installment) |
$ |
____________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
20. |
Salaries & Wages Payable |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
21. |
Taxes Payable |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
22. |
Other Payables |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
23. |
Mortgages |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
24. |
Auto Loans |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
25. |
Equipment Loans |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
|
|
|
|
26. |
Other Notes Payable |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
______________________ |
|
__________________ |
|
||
27. |
TOTAL LIABILITIES |
(add lines 19 through 26) |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 |
$ |
__________________ |
|
||
|
EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28. |
Equity |
(subtract line 27 from line 18) |
28 |
$ |
|
|
|
|
__________________ |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I declare under penalty of perjury that the foregoing and any attachments are true and correct.
PREPARED BY:
TITLE:
APPLICANT/LICENSEE SIGNATURE:
DATE:
LIC 403 (7/11) |
PAGE 1 OF 2 |

BALANCE SHEET
GENERAL INFORMATION: To complete the Balance Sheet LIC 403, first complete the LIC 403a, Balance Sheet Supplemental Schedule. The LIC 403a is a worksheet to be used in compiling the detailed information which is then totaled and displayed on the Balance Sheet, LIC 403. Submit the LIC 403a attached to the LIC 403.
Each applicant/licensee (sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation) must submit a LIC 403, and a LIC 403a. Information to be reported is to disclose all the entity’s assets and liabilities, not just those related to the operation of the care facility.
FOR SOLE PROPRIETORSHIPS - For a facility operated by a husband or wife individually, information reported must pertain to both, such as individual credit card balances which are listed either solely under one name or under both the husband and wife, and which may be unrelated to the facility’s actual operation or the person who will actually operate the facility.
FOR GENERAL PARTNERS - In addition to financial statements for the partnership, each general partner must file a personal Balance Sheet, LIC 403, accompanied with a LIC 403a, to reflect their individual financial position.
Information shown on the LIC 403 and LIC 403a is subject to verification. Additional documentation may be requested to support any or all of the Balance Sheet amounts reported.
INSTRUCTIONS: Include the required information at the top of this form to identify: 1) current date for the Balance Sheet, 2) entity name, (this is the sole proprietorship, partner, partnership or corporate name for whom the information is being reported) 3) facility name and 4) application/license number. Transfer the totals from the worksheet LIC 403a to the corresponding lines on the LIC 403. Below is a brief description of the type of information to be contained on each line.
ASSETS
Line #
1.Cash on hand, not deposited in a financial institution.
2.Cash in checking accounts.
3.CD’s, savings account(s) and all other like accounts.
4.Revenues receivable and all
5.Stocks, bonds or other securities.
6.Other current assets readily converted to cash, such as the cash surrender value of whole life insurance policies.
7.Add the amounts on lines 1 through 6 and enter here.
8.Real property is buildings, land and structures.
9.Land (developed or undeveloped) not already included on line 8.
10.Improvements to real property or leasehold improvements as appropriate.
11.Business or personal equipment, (other than that being leased).
12.Business or personal furniture and fixtures, as appropriate, (other than that being leased).
17.Add the amounts reported on lines 8 through 16 and enter here.
18.Add the amounts on line 7 and line 17 and enter here.
LIABILITIES
19.Credit Accounts (Open, Revolving and Installment).
20.Salaries, wages, bonuses and other benefits payable.
21.Federal, state or local income, sales or payroll taxes.
22.Other notes or payables not included above.
23.Current balances for all of the outstanding mortgages.
24.Vehicle loans.
25.Loans payable for furniture and equipment.
26.Other
27.Add the amounts on lines 19 through 26 and enter here.
EQUITY
28.The equity is the difference between your total assets and total liabilities. Subtract line 27 from line 18 and enter here.
SIGNATURE BLOCK
The name of the preparer is to be printed in the space provided. The applicant or licensee is required to sign this form attesting to the financial information. Failure to sign, date and attest to the accuracy of the information reported on the Balance Sheet (LIC 403) shall constitute
LIC 403 (7/11) |
PAGE 2 OF 2 |
Document Specs
| Fact Number | Detail |
|---|---|
| 1 | This form is used by the California Department of Social Services, specifically within the Community Care Licensing division. |
| 2 | It is designed to report both assets and liabilities, not limited to those related to the care facility's operation. |
| 3 | The form comprises sections for current and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity. |
| 4 | Applicants or licensees, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations, are required to complete and submit the form. |
| 5 | For accurate completion, individuals must first fill out the LIC 403a, Balance Sheet Supplemental Schedule, which aids in compiling detailed information for the LIC 403. |
| 6 | Information on the balance sheet must encompass all entity assets and liabilities, extending beyond those directly associated with the care facility's operation. |
| 7 | The form concludes with a signature block where the preparer’s name, the applicant or licensee’s signature, and the date are entered to attest to the accuracy of the information, under penalty of perjury. |
Detailed Instructions for Writing California Balance Sheet
Filling out the California Balance Sheet form is a straightforward process but requires attention to detail. It's designed to summarize an entity's financial position, including assets, liabilities, and equity, at a specific point in time. Whether you're a sole proprietor, part of a partnership, or operating a corporation, completing this form accurately is vital for compliance and financial clarity. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate through the form without hassle.
- Start by entering the current date at the top of the form where indicated.
- Fill in the Entity Name. This should be the name of the sole proprietor, partnership, or corporation as applicable.
- Provide the Facility Name if different from the Entity Name.
- Input the Application/License Number associated with your operation.
- Under Current Assets, itemize your assets beginning with cash on hand and cash in financial institutions, followed by CDs & other like accounts, short-term receivables & notes, stocks & bonds, and any other current assets. Each should be recorded in their respective lines with the dollar amount.
- Total the amounts listed under Current Assets and record the sum on the line provided for Total Current Assets.
- In the Long-term Assets section, list the value of real property, land (not included in real property), improvements, equipment, furniture & fixtures, and any other long-term assets, filling each line with the appropriate amounts.
- Add up the values in the Long-term Assets section to find the Total Long-term Assets, and enter this amount in the designated space.
- Sum the Total Current Assets and Total Long-term Assets to determine your Total Assets, and write this amount where indicated.
- Move to the Liabilities section and list your liabilities starting with credit accounts, salaries & wages payable, taxes payable, other payables, mortgages, auto loans, equipment loans, and any other notes payable, entering each amount on the appropriate line.
- Total your liabilities and record this amount in the space provided for Total Liabilities.
- Subtract Total Liabilities from Total Assets to calculate your Equity. Enter this figure in the designated space.
- Print the name of the form's preparer in the space provided.
- The applicant or licensee must sign and date the form, attesting to the accuracy of the information provided.
Upon completing the form, ensure that you attach the required LIC 403a, Balance Sheet Supplemental Schedule. Review all details for accuracy before submission, as this document is a legal statement of your financial position. Accurate and honest representation of your financial status on this form is crucial, not only for regulatory compliance but also for providing a clear picture of your entity's financial health.
Things to Know About This Form
What is the purpose of the California Balance Sheet form?
The California Balance Sheet form, known officially as LIC 403, is a critical document used by the California Department of Social Services, Community Care Licensing Division. Its primary purpose is to disclose the complete financial status of an entity, including all assets and liabilities. This encompasses both current and long-term financial positions. Entities such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations, especially those in the care facility industry, need to submit this form. Moreover, it aims to ensure that the entity has the financial stability required for the operation of care facilities, promoting the welfare and protection of those in care.
How do you complete the LIC 403 and LIC 403a forms?
To accurately complete the LIC 403, you must first fill out the LIC 403a, which serves as a supplemental schedule. This process involves compiling detailed information about your entity's financial situation, including in-depth data about assets and liabilities. The LIC 403a aids in organizing this data, which is then summarized and transferred to the LIC 403 form. Ensure you include the essential information like the current date, entity name, facility name, and application/license number at the top of the form. Remember to precisely calculate the totals for both assets and liabilities, as these figures are crucial for determining the entity's financial health.
Who is required to submit the LIC 403 and LIC 403a forms?
Both the LIC 403 and LIC 403a forms must be submitted by applicants or licensees of care facilities. This requirement applies to various types of ownership structures including:
- Sole Proprietorships: If the care facility is operated by either a husband or wife, information about both individuals must be reported.
- General Partnerships: Each general partner is obligated to submit their individual balance sheet alongside the partnership's financial statement.
- Corporations: Corporate entities must provide a comprehensive report of their financial status through these forms.
What types of assets and liabilities should be reported on these forms?
The LIC 403 and LIC 403a forms require detailed reporting of both assets and liabilities. Assets are divided into current and long-term categories, including but not limited to cash on hand, bank accounts, stocks, bonds, real property, and equipment. Liabilities encompass a wide range of financial obligations like credit accounts, salaries and wages payable, taxes payable, mortgages, and loans. It's important to accurately report all relevant financial obligations and resources to provide a comprehensive overview of the entity's financial health.
What happens if you do not accurately complete or submit the LIC 403 and LIC 403a?
Failure to accurately complete or submit the LIC 403 and the accompanying LIC 403a results in non-compliance with the requirements set by the California Department of Social Services, Community Care Licensing Division. This can lead to the rejection of your report, delaying or even jeopardizing the approval of your application or renewal for operating a care facility. It’s crucial to ensure all information is true, correct, and fully representative of your financial situation to avoid such issues.
Are there penalties for providing incorrect information on the California Balance Sheet form?
Yes, providing incorrect information on the California Balance Sheet form, either intentionally or due to negligence, can lead to serious consequences. Since the form must be signed under penalty of perjury, any falsehoods or inaccuracies are considered legal violations. Penalties may include the denial of your application or license, legal repercussions, and potentially criminal charges for perjury. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to provide accurate and truthful information when completing these forms.
Common mistakes
When filling out the California Balance Sheet form, it's crucial to avoid common mistakes to ensure the process goes smoothly. Here are ten of them:
- Not providing the current date at the top of the form, which is essential for identifying when the balance sheet was prepared.
- Omitting the entity name, facility name, or application/license number, which are necessary for proper identification and processing.
- Failure to attach the LIC 403a, Balance Sheet Supplemental Schedule, which is required to give detailed information that supports the balance sheet.
- Incorrectly calculating total assets, often due to simple arithmetic errors or not properly adding lines 1 through 6 for current assets and lines 8 through 16 for long-term assets.
- Leaving out or inaccurately reporting current assets, such as cash on hand or in financial institutions, which can significantly affect the balance sheet’s accuracy.
- Misunderstanding what qualifies as a long-term asset, leading to incorrect classifications between current and long-term sections.
- Misreporting liabilities, such as omitting outstanding loans or incorrectly detailing credit accounts, which can misrepresent the entity's financial health.
- Failure to calculate equity correctly by not subtracting total liabilities from total assets, a crucial step in determining the entity's net worth.
- Forgetting to sign and date the form, as required under the penalty of perjury, which attests to the truthfulness and accuracy of the information provided.
- Not utilizing the instructions on the reverse of the form or the detailed guidance for the LIC 403a, which can lead to incomplete or incorrect reporting of financial information.
Avoiding these mistakes not only helps in accurately presenting the financial position of the entity but also ensures compliance with the requirements of the California Department of Social Services Community Care Licensing Division.
Documents used along the form
When it comes to ensuring the financial transparency and stability of an entity, especially in sensitive sectors like health and human services, the California Balance Sheet form (LIC 403) plays a pivotal role. This form captures a comprehensive snapshot of the entity's financial position, detailing assets and liabilities which are crucial for assessing the entity's health. However, to furnish a complete view or meet specific regulatory requirements, additional documents often accompany the Balance Sheet form. These documents serve to provide more detail, specify operations, or offer further financial clarity. Below is a list of such documents and a brief explanation of their relevance and contents.
- LIC 403a - Balance Sheet Supplemental Schedule: This worksheet is essential to the LIC 403 as it gathers detailed information about the assets and liabilities to be summarized on the Balance Sheet. It aids in the process of breaking down the numbers, offering a clearer perspective on each category of the balance sheet.
- Profit and Loss Statement: This document complements the Balance Sheet by detailing the entity's operational revenues, costs, and expenses over a period. It's crucial for understanding the entity's operational efficiency and profitability, painting a fuller picture of financial health beyond the static snapshot of assets and liabilities.
- Cash Flow Statement: While the Balance Sheet provides a moment-in-time view, the Cash Flow Statement shows how much actual cash an entity has generated or used in a period. It's vital for assessing the liquidity and long-term solvency of the entity.
- Statement of Owner's Equity: This document details changes in the equity portion of the balance sheet, showing contributions, withdrawals, and the impact of profits or losses. It's particularly relevant in understanding how the owner's equity has evolved over time.
- Tax Returns: Recent tax returns may be required to corroborate the financial figures reported on the Balance Sheet and other documents. They serve as an official record of the entity's financial activities as reported to tax authorities.
- Loan Agreements and Schedules: If the entity has loans listed as liabilities, providing copies of the loan agreements and repayment schedules can offer insights into the terms, rates, and maturity of these obligations. It helps in assessing the entity's debt service capabilities and long-term financial commitments.
Together, these documents create a multidimensional view of an entity's financial situation, beyond what a single Balance Sheet can convey. For entities involved in the operation of care facilities in California, such comprehensive financial documentation is not just about regulatory compliance; it also instills confidence among stakeholders about the entity's fiscal responsibility and sustainability. Understanding and properly preparing these documents is indispensable for demonstrating financial health and operational viability.
Similar forms
The Income Statement, sometimes called a Profit and Loss Statement, bears similarities to the California Balance Sheet in how it represents financial positions, but it focuses specifically on revenues, expenses, and profit over a certain period. Unlike the balance sheet, which provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity at a single point in time, the income statement tracks financial performance across time, showcasing how effectively a company generates profit from operations. Both documents, however, are essential for understanding a business’s financial health, where the balance sheet shows what the company owns and owes, and the income statement shows how the company has performed financially during a period.
A Statement of Cash Flows is akin to the California Balance Sheet as both offer insights into financial health but from different angles. The Statement of Cash Flips details the cash generated and used by a company during a specific period, categorized into operations, investing, and financing activities. While the balance sheet accounts for cash on hand as part of current assets, the Statement of Cash Flows explains how those cash positions change over time due to business activities, providing a dynamic view of a company’s liquidity and solvency that complements the stationary snapshot provided by the balance sheet.
The Statement of Owners’ Equity, also known as the Equity Statement, complements the information found on the California Balance Sheet by delving into changes in equity throughout the accounting period. Whereas the balance sheet shows the ending equity balance, the Equity Statement breaks down equity adjustments such as investments by owners, distributions to owners, and the company's net income or loss. Together, these documents paint a complete picture of how company operations affect owner equity, offering stakeholders detailed insights into the company’s financial evolution over time.
The Statement of Financial Position, commonly understood in the nonprofit sector, is similar to the California Balance Germane to for-profit balance sheets, it lists assets, liabilities, and net assets (equivalent to equity in for-profit organizations) as of a specific date. It reflects how resources are allocated within a nonprofit, providing a snapshot of financial status much like the balance sheet does for businesses. By comparing assets against liabilities, stakeholders can gauge the net assets available for future use by the organization, making it a crucial tool for financial assessment alongside the balance sheet for understanding overall financial health.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the California Balance Sheet form, it is essential to approach the task with care and attention to detail. Missteps can cause delays or issues with your submission. To ensure accuracy and completeness, here are key dos and don'ts to consider:
- Do carefully read the instructions on the reverse side before starting. They provide valuable guidance on how to properly fill out the form.
- Do ensure that you include the current date at the top of the form where indicated. This reflects the date for which the balance sheet is relevant.
- Do accurately enter the entity name, facility name, and application/license number. These details are critical for identification purposes.
- Do complete the LIC 403a, Balance Sheet Supplemental Schedule, before working on the LIC 403 form. It helps in compiling the detailed information necessary for the balance sheet.
- Do accurately transfer totals from LIC 403a to the corresponding lines on LIC 403. This ensures consistency between the supplemental schedule and the balance sheet.
- Do disclose all assets and liabilities of the entity, not just those directly related to the care facility's operation. This provides a comprehensive view of your financial position.
- Do remember to sign and date the form. An unsigned form could be rejected or returned, causing delays in processing.
- Don't overlook the requirement to submit both the LIC 403 and LIC 403a forms. Both are necessary for a complete submission.
- Don't enter incomplete or estimated figures. Use the actual, most up-to-date numbers to ensure accuracy.
- Don't neglect to attach additional documentation if required. Sometimes, supporting documents may be necessary to verify the information provided on the balance sheet.
By following these guidelines, you can confidently complete the California Balance Sheet form, ensuring a smooth and efficient submission process. Remember, accuracy, and clarity in your financial reporting are crucial for compliance and the success of your application.
Misconceptions
Many people find the California Balance Sheet form, required by the California Department of Social Services, a bit intimidating at first glance. However, some of the most common misconceptions can be easily clarified, making it more approachable and understandable.
- Only care facilities' assets and liabilities need to be reported: It's a common mistake to think that you should only report assets and liabilities directly related to the operation of the care facility. In reality, all assets and liabilities of the entity must be disclosed, not just those connected to the care facility's operations.
- The balance sheet is only for corporations: This misconception might lead some to believe that sole proprietorships or partnerships are exempt from this requirement. However, every applicant/licensee, regardless of the business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation), must submit a balance sheet.
- Personal information is not required for partnerships: In fact, for general partnerships, not only is a financial statement for the partnership necessary, but each general partner must also submit a personal balance sheet to reflect their individual financial position.
- Information reported does not need verification: There’s a false belief that the information provided on the LIC 403 and LIC 403a forms will not be cross-checked. Contrary to this belief, all information shown on these forms is subject to verification, and additional documentation may be requested.
- Cash in financial institutions should not include checking accounts: Another error is thinking that cash in financial institutions refers only to savings accounts and CDs, excluding checking accounts. Checking account balances should indeed be included under "Cash in Financial Institutions."
- Real property includes only buildings: While real property does include buildings, this category also encompasses land and any structures on that land, not just the buildings themselves.
- Only business-related assets should be listed: Some believe that if they own personal assets, like a car or life insurance, these shouldn't be included. However, other current assets that can be readily converted to cash, including personal assets like the cash surrender value of whole life insurance policies, should be listed.
- Listing liabilities is optional: Every bit as important as listing assets, disclosing all liabilities accurately is mandatory and not at the discretion of the entity completing the form.
- Equity calculation is complex: The equation for determining equity might seem daunting at first glance, but it is simply the difference between total assets and total liabilities. It’s more straightforward than most realize.
- Signature compliance is a formality: Failing to sign, date, and attest to the accuracy of the information reported on the Balance Sheet (LIC 403) is a serious misstep. It can result in non-compliance and the rejection of the report, contrary to the belief that it’s just a mere formality.
Understanding these misconceptions can vastly simplify the process of completing the California Balance Sheet form. Being thorough and accurate in reporting can assist applicants and licensees in meeting the legal requirements without undue stress.
Key takeaways
When filling out the California Balance Sheet form, it’s important to understand what information is required and how it should be presented. Below are key takeaways to guide you through the process:
- Complete the LIC 403a first: Before you start filling out the LIC 403 form, you must fill out the LIC 403a. The LIC 403a serves as a supplementary schedule that helps organize the detailed information about your assets and liabilities that will be summarized on the LIC 403.
- Present accurate entity information: At the top of the form, clearly state the current date, entity name (this can be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporate name), facility name, and application/license number.
- Report all assets and liabilities: Disclose all assets and liabilities of the entity, not just those directly related to the operation of the care facility. This includes both current and long-term assets and liabilities.
- Distinguish between current and long-term assets: Current assets are cash or other assets that can be readily converted into cash within one year, while long-term assets are items like real property, equipment, and furniture that have a longer life span.
- Include all forms of cash: When reporting assets, distinguish between cash on hand, funds in financial institutions, CDs, and similar accounts. Stocks, bonds, and other securities should also be reported.
- Accurately categorize liabilities: Clearly differentiate between various liabilities such as open credit accounts, salaries and wages payable, taxes payable, and any loans, including mortgages and equipment loans.
- Calculate total assets and liabilities correctly: After listing all individual assets and liabilities, sum them up correctly to find the total current assets, total long-term assets, and total liabilities.
- Determine equity: Equity is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from the total assets. This value should be correctly entered in the equity section of the form.
- Verification and documentation: Be prepared to provide additional documentation to support the amounts reported on your balance sheet, as the information may be subject to verification.
- Signature is mandatory: The form requires the signature of the applicant or licensee, attesting to the financial information’s accuracy. Failure to sign the LIC 403 will lead to non-compliance and rejection of the report.
Understanding these components of the California Balance Sheet and correctly completing both the LIC 403 and LIC 403a are critical steps in ensuring compliance with the California Department of Social Services Community Care Licensing requirements.
Discover More PDFs
Ca Efile Waiver - Consult the payment instructions in your tax booklet carefully to avoid any mistakes when fulfilling your payment obligations.
What Is Form 100 - Optimize your tax return in California by employing Form 3540 to declare carryovers from specific repealed tax credits.
Death of Joint Tenant - It clarifies the shift in ownership, ensuring that the surviving joint tenant(s) can assert their property rights unequivocally.